
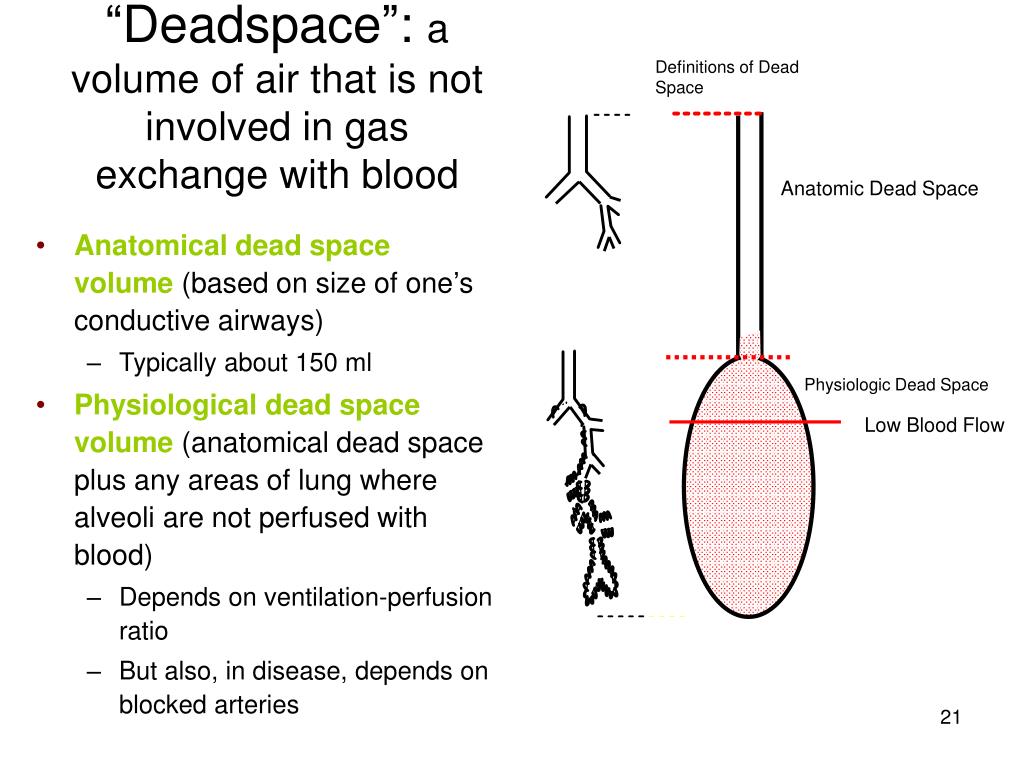
Why is anatomical dead space?Īnatomical dead space occurs naturally in areas of the lungs that don’t come in contact with alveoli (like the trachea). The physiological dead space is the combination of anatomic and alveolar dead space. Thus, only one alveolus is receiving ventilation and perfusion (alveolus 2) alveolus 1 and 3 are being ventilated but not perfused (ie, alveolar dead space). Is alveolar dead space the same as physiological dead space? The anatomical dead space is the total volume of the conducting airways from the nose or mouth to the terminal bronchioles, and in ventilated infants includes the apparatus dead space (endotracheal tube and flow sensor). The physiological dead space is the anatomical dead space plus alveolar dead space. … In healthy lungs where the alveolar dead space is small, Fowler’s method accurately measures the anatomic dead space by a nitrogen washout technique. I literally know nothing more on the subject.Anatomical dead space is that portion of the airways (such as the mouth and trachea to the bronchioles) which conducts gas to the alveoli. Treat a pulmonary embolus or anything perfusion limited, assuming Pressure difference across HEALTHY lung (in this instance) willĬause a higher oxygen saturation than typical in the remainingĬapillary beds not blocked by the embolus. Good would adding more O2 do? Again, increasing the partial Shows equilibration of gases by the end of the capillary, so what This is tricky, because perfusion limitation In the case of a pulmonary embolism, there is Blasting them with O2 will do little.ĭead space or perfusion limitation on the other hand does YouĪre not doing anything to ameliorate the initial problem: bad Such people cannot be treated with 100% O2 very successfully. Participating in gas exchange for the reasons I just mentioned.Īlso think of pulmonary fibrosis, where thickness is increased. Surface area is diminished because of less healthy lung tissue Little fibrosis in emph., it's not a thickness issue). Partial pressure of the gas of interest on both sides (in the blood The surface area available for exchange, and the difference in Membrane/solubility of the gas, the thickness of this interface, There is a limitation to diffusion because theĮndothelial alveolar interface is destroyed in emphysema. Shunts are diffusion limited byĭefinition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
